The SUPRAX® 8488 product range includes disc sight glasses, reflex and transparent level gauge glasses (also as high-pressure)
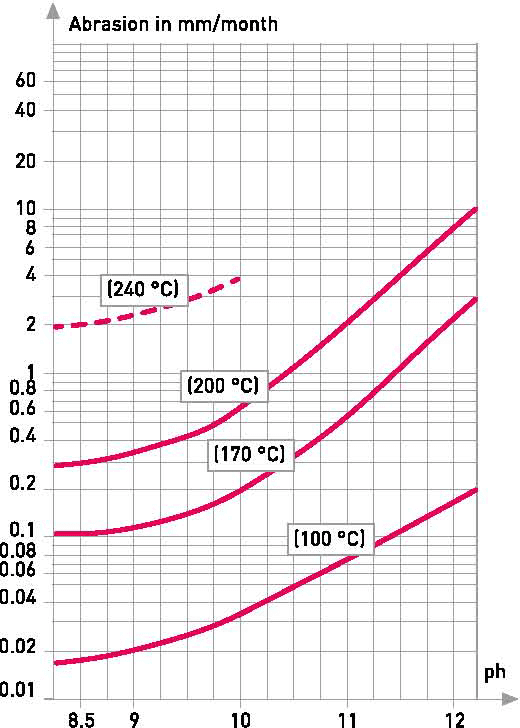
The specially developed SUPRAX® 8488 borosilicate glass used for the Maxos® sight glasses guarantees superior chemical resistance. The low expansion of the glass, combined with thermal prestressing, creates high resistance to sudden temperature changes.
Technical properties
| Coefficient of expansion α 20°C / 300°C | 4.1 x 10–6 K–1 |
|---|---|
| Max. operating temperature | 300°C / 572°F |
| Thermal shock resistance as per ISO 720 | ΔT 230°C |
| Transformation temperature | 545°C |
| Glass temperature for the viscosities dPas (Poise) | 1013.0 560°C / 1040°F 107.6 800°C / 1472°F 104.0 1210°C / 2210°F |
| Density at 25°C | 2.3 g/cm³ |
| Modulus of elasticity | 67 x 10³ N/mm² |
| Poisson’s ratio μ | 0.20 |
| Thermal conductivity λ at 90°C | 1.2 W/(m·K) |
| Refractive index nd (λ = 587.6 nm) | 1.482 |
| Photoelastic parameter K | 3.2 x 10–6 mm²/N |
It depends on the proportion: The high amount of silicon dioxide (SiO2) and boric acid (B2O3) characterizes this type as a glass former. The proportion of boric acid influences the glass properties in a specific way: We use a proportion of only 11.5 %. This makes it more stable in comparison to glasses with an even higher boric acid content. In addition, the embedding in the structural network ensures extremely high chemical resistance.
